In India, Nifty and Bank nifty are two widely traded liquid contracts. Both are available in futures and options.
Nifty index tracks the 50 largest listed companies in India and Bank nifty tracks top 12 Indian banking stocks. In this article, you will learn different ways available in the market to trade Nifty.
Obviously, you will not be allowed to trade the actual index NIFTY. We have different products available for trading which derived their value from NIFTY. They are called derivatives.
Futures and options are two derivative contracts as they derive value from an underlying asset. In the case of nifty futures and options, they derive value from Nifty index being the underlying asset.
Which means, if the value of the Nifty index rises, then the value of its future and option contracts also goes up. Similarly, if the Nifty index falls, the price of future and option contracts declines.
What moves the NIFTY 50 price?
NIFTY 50 price moves based on how 50 stocks which are part of the index performs. The main criteria which defines how nifty performs is supply and demand of the underlying 50 stocks.
Here are the most important factors which impact supply and demand which decide the performance of nifty.
- Individual 50 companies share prices which are part of Nifty, particularly the large ones like reliance, HDFC bank, TCS, banking and IT stocks.
- Earning reports of these 50 companies
- Strength and weakness of indian rupees against USD and other important currencies
- Economic events such as Reserve Bank of India (RBI)‘s policies, Fed decisions, inflation and other announcements
- News releases
- Political decisions
- Wars
- Global economy
We have two financial instruments available in the NSE to trade the nifty index: futures and options.
Nifty Futures
Nifty future contracts come with a 3 months trading cycle. This is why you will always find 3 nifty futures contracts available for trade from your trading window.
The Nifty future contract expiring on the last Thursday of the current month end is known as the near month. Contract expiring next month’s last Thursday is referred to as the next month and the far month is a contract which expires next to the next month’s end.
The next month contract is also known as mid month.
For instance, the current month when we are writing this article is December 2023. So the contract which expires on 28th December is known as the near month. The Next month contract will be the one which expires on 25th January 2024. Similarly, the contract that expires on 29th February 2024 will be known as the far month contract.
New contract will be introduced on the trading day following the expiry of the near month contract. Which means on 29th December after expiry of December 2023 contracts, a new contract will be introduced expiring on 28th March 2023.
After introduction of the new contract, the contract that is expiring on 25th jan 2024 will be treated as near month, contract expiring on 29th february 2024 will be known as the next month contract and the newly introduced contract with expiry date of 28th march 2023 will be referred to as far month contract.
As new contracts are introduced every month, at any point of time, you will always find 3 contracts available to trade.
Here is a screenshot showing how 3 active future contracts are available to trade after the December month expiry.
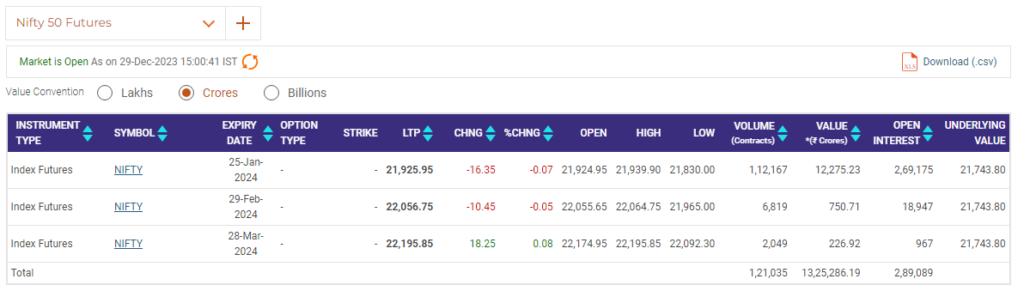
When does the nifty future expire?
Future contracts of the nifty index expire on the last Thursday of the expiry month.
For instance December future contracts of the nifty index will expire on 28th December 2023. From 29th December 2023, the January month expiry contracts will be considered as near the month and will expire on 25th January 2024, being the last Thursday of the January month.
In case the last Thursday is a trading holiday, then the contract will expire on the previous trading day. Which means, it will expire on the last wednesday of the month if its a trading day.
The permitted lot size for futures contracts on the nifty index is 50. Which means if the future price is Rs 21,885 the money required to trade is Rs 10,94,250. Depending on the broker’s margin facility, a trader may be asked to trade with less money.
In order to avoid erroneous order entry nifty futures has an operating range of +/- 10%.
NIFTY Options
Option is a derivative contract which derives its value from an underlying asset. In the case of nifty options, the underlying asset is a nifty index.
An option contract gives the right but not the obligation to buy or sell the underlying asset. In an option contract, we have two parties: buyer and seller.
Buyer of an option pays a fee (premium) for the right and the seller accepts the obligation for which he/she receives the premium. In exchange, the premium keeps changing based on the demand and supply dynamics.
A person who buys the option is known as option buyer and he is long in the option. The seller on the other hand, known as writer, is said to be short in the option.
We have two types of options traded in the stock exchanges: call and put.
At any point in time, you will find option contracts for up to 5 years. Here are the option contracts available for you to trade;
- 4 weekly expiry contracts
- 3 consecutive month contracts
- 3 quarterly months of the cycle (March / June / September / December)
- 8 following semi-annual months of the cycle (June / December)
On the trading day following the expiry date, new contracts will be introduced so that at any point of time you will have option contracts for 5 years.
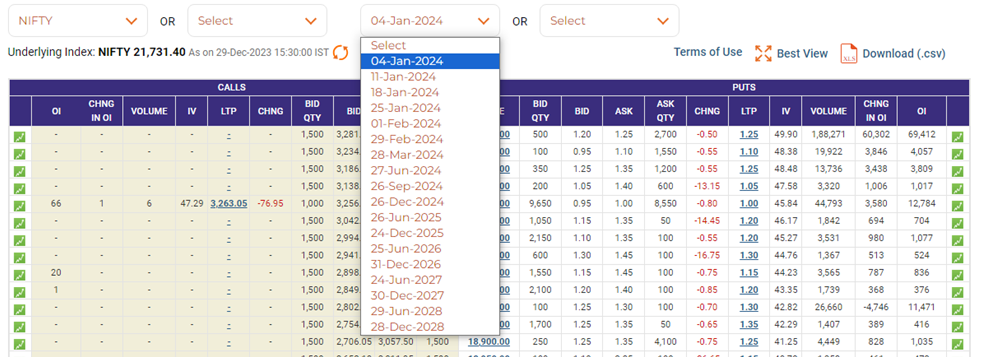
Like nifty future contracts, options expire on the last Thursday of the expiry month / week. If last Thursday is a trading holiday, then the contract expires on the previous trading day.
The permitted lot size for nifty option contracts is 50. Which means if the premium is Rs 100, then to buy one lot, you have to pay Rs 5,000.
Futures and options have expiry due to which many long term investors prefer to bet for exchange traded funds (ETF) instead of putting their money in derivative contracts.
We have ETFs for nifty, which invest in all the 50 underlying stocks in the same proportion as they are in Nifty. All these ETFs are traded in stock exchanges.
ETFs allow investors to diversify their portfolio at one shot at a low cost.
What is GIFT Nifty and where is it traded?
GIFT Nifty is rebranded from SGX Nifty. GIFT Nifty is a derivative contract of the NIFTY index listed in NSE international exchange (NSE IX) in Gujarat International Finance Tech City (GIFT), Gandhinagar.
It’s a collaboration of NSE IX and Singapore Exchange (SGX) to allow investors in India and around the world to trade in Nifty contracts listed on NSE IX.
GIFT city is India’s first International Financial Service Centre (IFSC).
Here are three things you can do to improve your success rate in trading NIFTY futures and options:
- Learn technical analysis, candlesticks, trading signals and chart patterns.
- Find the best trading style that suits you the most. Trading style includes day trading, scalping, swing trading and position trading.
- Follow market and industry news to understand the impact of it on the stock market.
Disclaimer: In addition to the disclaimer below, please note, this article is not intended to provide investing or trading advice. Trading in the stock market and in other securities entails varying degrees of risk, and can result in loss of capital. Most investors and traders lose money. Readers seeking to engage in trading and/or investing should seek out extensive education on the topic and help of professionals.